Cataract, Refractive
All-day Near Vision in View
Aceclidine eye drop may provide long-lasting effects for presbyopia patients.

Howard Larkin
Published: Monday, July 3, 2023
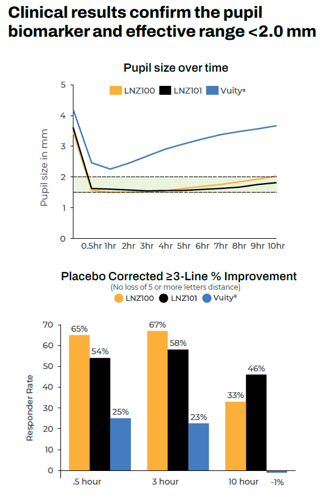
A presbyopia-correcting eye drop based on the miotic compound aceclidine produced three lines or more of near vision improvement for up to 10 hours in a recent clinical trial, reported Dr Marc Odrich.
He emphasised that these results improve substantially on presbyopia-treating eye drops based on pilocarpine or carbachol.
In a phase 2 clinical trial comparing aceclidine alone and aceclidine plus brimonidine with placebo, 73% and 64% of patients receiving the aceclidine preparations, respectively, saw three or more lines of improvement in near vision with less than five letters of distance vision lost at three hours, and 37% and 48% did so at 10 hours, compared with single-digit gains for the placebo at all checkpoints.
Formulated to extend the effect’s duration, the aceclidine-brimonidine solution performed better than aceclidine alone after nine hours. And once corrected for placebo effect, these efficacy findings are multiples of some drugs already on the market, Dr Odrich noted.
“We’re talking about a strong miotic,” he said. “We have high efficacy all the way out to 10 hours.”
Two phase 3 studies of the aceclidine formulations are underway. They include a range of patients from age 45 to 75 years, refractions ranging from -4.0 D to +1.5 D spherical equivalent, and post-LASIK and pseudophakic patients.
The keys to aceclidine’s effectiveness are its strength and selectivity as a miotic, Dr Odrich explained. Miotics improve near vision by restricting the pupil to create a pinhole effect, with depth of focus increasing rapidly below the Rayleigh limit, which is about 2.0 mm.
“For increased depth of focus, a sub-2.0 mm pupil is essential,” and aceclidine produces one for about 10 hours, he said.
However, many miotics that constrict the iris sphincter also constrict the ciliary muscle, moving the lens anteriorly. This induces a myopic shift of about -1.25 D, which may require distance vision spectacles to correct, Dr Odrich said. Aceclidine is much more selective for the iris sphincter—by a factor of 28:1 compared with approximately 5:1 for carbochol and about 1.5:1 for pilocarpine. As a result, aceclidine induces much less myopia, about -0.13 D.
“We have identified the ideal pupil diameter and, at the same time, the drug that flexes the right muscle,” Dr Odrich said.
In a separate presentation, Dr Steven J Dell noted presbyopia eye drops currently on the market mostly do not constrict pupils below 2.3 mm and induce myopia. These issues may have contributed to the fall in prescriptions for Vuity (AbbVie)—a pilocarpine solution—which peaked in the US at around 5,800 per week in April 2022 but has since fallen to about 1,600 per week, of which roughly 1,000 are refills.
Dr Dell noted aceclidine does keep the pupil below 2.0 mm, the threshold for improving near vision. “We need stronger, pupil-selective miotics, and these are on the way.”
Dr Odrich presented at the Eyecelerator event at the 2023 ASCRS annual meeting in San Diego, US.
Steven J Dell MD is an ophthalmologist in Austin, Texas, US. He disclosed a relationship with Lenz Therapeutics. steven@dellmd.com
Marc Odrich MD is chief medical officer of Lenz Therapeutics, Del Mar, California, US, and associate professor and director of UVA LASIK at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, US. contact@lenz-tx.com
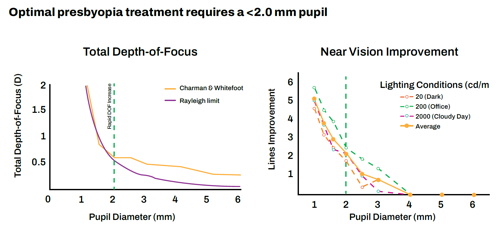
Source: Charman, W Neil. 2019. “Pinholes and Presbyopia: Solution or Sideshow?” Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 39(1): 1–10. Wiley
Online Library. doi.org/10.1111/opo.12594. Near Vision Improvement: Psychophysical visual acuity was tested using an eight orientation, forced-choice paradigm, and maximum contrast Landolt C targets while independently controlling pupil size, defocus levels, and luminance. Pupil was manipulated with eight artificial pupils (1, 1.3, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 6 mm) imaged onto the subjects’ dilated entrance, N=2.
All products except Vuity are investigational. Studies presented were not head-to-head and study designs will vary, see clinicaltrials.gov identifiers below
Data Sources: LENZ INSIGHT (NCT05294328) Phase 2 study results from website as of 1/25/23, Vuity Product Insert from website as of 2/13/23.
Latest Articles
Towards a Unified IOL Classification
The new IOL functional classification needs a strong and unified effort from surgeons, societies, and industry.
Organising for Success
Professional and personal goals drive practice ownership and operational choices.
Update on Astigmatism Analysis
Is Frugal Innovation Possible in Ophthalmology?
Improving access through financially and environmentally sustainable innovation.
iNovation Innovators Den Boosts Eye Care Pioneers
New ideas and industry, colleague, and funding contacts among the benefits.
José Güell: Trends in Cornea Treatment
Endothelial damage, cellular treatments, human tissue, and infections are key concerns on the horizon.
Making IOLs a More Personal Choice
Surgeons may prefer some IOLs for their patients, but what about for themselves?
Need to Know: Higher-Order Aberrations and Polynomials
This first instalment in a tutorial series will discuss more on the measurement and clinical implications of HOAs.
Never Go In Blind
Novel ophthalmic block simulator promises higher rates of confidence and competence in trainees.